Android N平臺
0 init進程的主要職責
- init如何創建zygote。
- init的屬性服務是如何工作的。
1 init.cpp分析
涉及源碼位置:
aosp/system/core/init/init.cpp
aosp/system/core/rootdir/init.rc
aosp/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
1.1從init進程的入口函數main()開始分析
init進程的main()函數會執行兩次,分別是第一階段和第二階段,main函數會進入兩次,只是兩次進去執行的代碼不一樣
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//由于ueventd watchdogd是公用代碼,所以啟動的時候根據文件名來判斷是哪個進程
//和ueventd守護進程相關
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "ueventd")) {
return ueventd_main(argc, argv);
}
//和watchdogd守護進程相關
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "watchdogd")) {
return watchdogd_main(argc, argv);
}
// Clear the umask.
umask(0);
//添加環境變量
add_environment("PATH", _PATH_DEFPATH);
bool is_first_stage = (argc == 1) || (strcmp(argv[1], "--second-stage") != 0);
//創建文件夾,掛載設備,和linux相關
// Get the basic filesystem setup we need put together in the initramdisk
// on / and then we'll let the rc file figure out the rest.
if (is_first_stage) {
mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755");
mkdir("/dev/pts", 0755);
mkdir("/dev/socket", 0755);
mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL);
#define MAKE_STR(x) __STRING(x)
mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, "hidepid=2,gid=" MAKE_STR(AID_READPROC));
mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL);
}
// We must have some place other than / to create the device nodes for
// kmsg and null, otherwise we won't be able to remount / read-only
// later on. Now that tmpfs is mounted on /dev, we can actually talk
// to the outside world.
//重定向標準輸入/輸出/錯誤輸出到/dev/_null_
open_devnull_stdio();
//對klog進行初始化,設置klog level為NOTICE,所以可以將NOTICE級別的log輸出,而INFO級別的log就打印不出來
//<http://blog.csdn.net/fu_kevin0606/article/details/53339001>
//初始化klog
klog_init();
//設置klog的級別為NOTICE
klog_set_level(KLOG_NOTICE_LEVEL);
NOTICE("init %s started!\n", is_first_stage ? "first stage" : "second stage");
if (!is_first_stage) {//第二階段執行該代碼
// Indicate that booting is in progress to background fw loaders, etc.
close(open("/dev/.booting", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_CLOEXEC, 0000));
//屬性服務初始化,接下來會分析
property_init();
// If arguments are passed both on the command line and in DT,
// properties set in DT always have priority over the command-line ones.
process_kernel_dt();
process_kernel_cmdline();
// Propagate the kernel variables to internal variables
// used by init as well as the current required properties.
export_kernel_boot_props();
}
//初始化SELinux,加載策略文件
// Set up SELinux, including loading the SELinux policy if we're in the kernel domain.
selinux_initialize(is_first_stage);
// If we're in the kernel domain, re-exec init to transition to the init domain now
// that the SELinux policy has been loaded.
if (is_first_stage) {
if (restorecon("/init") == -1) {
ERROR("restorecon failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
security_failure();
}
char* path = argv[0];
//設置第二階段的參數
char* args[] = { path, const_cast<char*>("--second-stage"), nullptr };
//當init是第一階段,要通過execv重啟init進程,進入init的第二階段
if (execv(path, args) == -1) {
ERROR("execv(\"%s\") failed: %s\n", path, strerror(errno));
security_failure();
}
}
// These directories were necessarily created before initial policy load
// and therefore need their security context restored to the proper value.
// This must happen before /dev is populated by ueventd.
NOTICE("Running restorecon...\n");
restorecon("/dev");
restorecon("/dev/socket");
restorecon("/dev/__properties__");
restorecon("/property_contexts");
restorecon_recursive("/sys");
epoll_fd = epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC);
if (epoll_fd == -1) {
ERROR("epoll_create1 failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
signal_handler_init();
property_load_boot_defaults();
export_oem_lock_status();
//啟動屬性服務
start_property_service();
const BuiltinFunctionMap function_map;
Action::set_function_map(&function_map);
//將`service`,`on`,`import`分為3個section
Parser& parser = Parser::GetInstance();
parser.AddSectionParser("service",std::make_unique<ServiceParser>());
parser.AddSectionParser("on", std::make_unique<ActionParser>());
parser.AddSectionParser("import", std::make_unique<ImportParser>());
//解析init.rc配置文件入口
parser.ParseConfig("/init.rc");
ActionManager& am = ActionManager::GetInstance();
am.QueueEventTrigger("early-init");
// Queue an action that waits for coldboot done so we know ueventd has set up all of /dev...
am.QueueBuiltinAction(wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done");
// ... so that we can start queuing up actions that require stuff from /dev.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng_action, "mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(set_mmap_rnd_bits_action, "set_mmap_rnd_bits");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(keychord_init_action, "keychord_init");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(console_init_action, "console_init");
// Trigger all the boot actions to get us started.
am.QueueEventTrigger("init");
// Repeat mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng in case /dev/hw_random or /dev/random
// wasn't ready immediately after wait_for_coldboot_done
am.QueueBuiltinAction(mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng_action, "mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng");
// Don't mount filesystems or start core system services in charger mode.
std::string bootmode = property_get("ro.bootmode");
if (bootmode == "charger") {
am.QueueEventTrigger("charger");
} else {
am.QueueEventTrigger("late-init");
}
// Run all property triggers based on current state of the properties.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers");
while (true) {
if (!waiting_for_exec) {
am.ExecuteOneCommand();
restart_processes();
}
int timeout = -1;
if (process_needs_restart) {
timeout = (process_needs_restart - gettime()) * 1000;
if (timeout < 0)
timeout = 0;
}
if (am.HasMoreCommands()) {
timeout = 0;
}
bootchart_sample(&timeout);
epoll_event ev;
int nr = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(epoll_wait(epoll_fd, &ev, 1, timeout));
if (nr == -1) {
ERROR("epoll_wait failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
} else if (nr == 1) {
((void (*)()) ev.data.ptr)();
}
}
return 0;
}
main函數里涉及不少東西,只是把當前知道的注釋了一下,以后補充,這里關注一下,屬性服務的啟動,以及對init.rc文件的解析.
1.2 屬性服務
Android中有很多屬性,是通過屬性服務(property service)來管理它們的.接著來分析屬性服務的代碼,從上面的init.cpp的main函數中涉及屬性服務的代碼有
property_init();
start_property_service();
從property_init()開始分析,該方法的主要工作是初始化屬性服務配置.位置在aosp/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
void property_init() {
if (property_area_initialized) {
return;
}
property_area_initialized = true;
//__system_property_area_init()函數是用來初始化屬性內存區域
if (__system_property_area_init()) {
return;
}
pa_workspace.size = 0;
pa_workspace.fd = open(PROP_FILENAME, O_RDONLY | O_NOFOLLOW | O_CLOEXEC);
if (pa_workspace.fd == -1) {
ERROR("Failed to open %s: %s\n", PROP_FILENAME, strerror(errno));
return;
}
}
接下來查看start_property_service函數的具體代碼:
void start_property_service() {
//創建一個非阻塞的socket,
property_set_fd = create_socket(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK,
0666, 0, 0, NULL);
if (property_set_fd == -1) {
ERROR("start_property_service socket creation failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
//使用listen函數對之前創建的socket進行監聽
listen(property_set_fd, 8);
register_epoll_handler(property_set_fd, handle_property_set_fd);
}
listen(property_set_fd, 8);中的8指屬性服務最多可以同時為8個試圖設置屬性的用戶提供服務.property_set_fd代表監聽
的端口(socket),這樣屬性服務就建立了.register_epoll_handler(property_set_fd, handle_property_set_fd)將property_set_fd
放入了epoll句柄中,用epoll來監聽property_set_fd:當property_set_fd中有數據到來時,init進程將用handle_property_set_fd
函數進行處理。(網上資料說:在linux新的內核中,epoll用來替換select,epoll最大的好處在于它不會隨著監聽fd數目的增長而降低效率。
因為內核中的select實現是采用輪詢來處理的,輪詢的fd數目越多,自然耗時越多,epoll還沒有研究過,抽時間學習一下).
當有property_set_fd這個socket有數據來時,就會產生調用到handle_property_set_fd方法,接著分析該方法:
static void handle_property_set_fd()
{
prop_msg msg;
int s;
int r;
struct ucred cr;
struct sockaddr_un addr;
socklen_t addr_size = sizeof(addr);
socklen_t cr_size = sizeof(cr);
char * source_ctx = NULL;
struct pollfd ufds[1];
const int timeout_ms = 2 * 1000; /* Default 2 sec timeout for caller to send property. */
int nr;
if ((s = accept(property_set_fd, (struct sockaddr *) &addr, &addr_size)) < 0) {
return;
}
/* Check socket options here */
if (getsockopt(s, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERCRED, &cr, &cr_size) < 0) {
close(s);
ERROR("Unable to receive socket options\n");
return;
}
ufds[0].fd = s;
ufds[0].events = POLLIN;
ufds[0].revents = 0;
nr = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(poll(ufds, 1, timeout_ms));
if (nr == 0) {
ERROR("sys_prop: timeout waiting for uid=%d to send property message.\n", cr.uid);
close(s);
return;
} else if (nr < 0) {
ERROR("sys_prop: error waiting for uid=%d to send property message: %s\n", cr.uid, strerror(errno));
close(s);
return;
}
r = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(recv(s, &msg, sizeof(msg), MSG_DONTWAIT));
if(r != sizeof(prop_msg)) {
ERROR("sys_prop: mis-match msg size received: %d expected: %zu: %s\n",
r, sizeof(prop_msg), strerror(errno));
close(s);
return;
}
switch(msg.cmd) {
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP:
msg.name[PROP_NAME_MAX-1] = 0;
msg.value[PROP_VALUE_MAX-1] = 0;
if (!is_legal_property_name(msg.name, strlen(msg.name))) {
ERROR("sys_prop: illegal property name. Got: \"%s\"\n", msg.name);
close(s);
return;
}
getpeercon(s, &source_ctx);
if(memcmp(msg.name,"ctl.",4) == 0) {
// Keep the old close-socket-early behavior when handling
// ctl.* properties.
close(s);
if (check_control_mac_perms(msg.value, source_ctx)) {
#ifdef MTK_INIT
//INFO("[PropSet]: pid:%u uid:%u gid:%u %s %s\n", cr.pid, cr.uid, cr.gid, msg.name, msg.value);
#endif
handle_control_message((char*) msg.name + 4, (char*) msg.value);
} else {
ERROR("sys_prop: Unable to %s service ctl [%s] uid:%d gid:%d pid:%d\n",
msg.name + 4, msg.value, cr.uid, cr.gid, cr.pid);
}
} else {
//check_perms:檢測設置系統屬性的權限,允許返回1,否則返回0
if (check_perms(msg.name, source_ctx)) {
#ifdef MTK_INIT
//INFO("[PropSet]: pid:%u uid:%u gid:%u set %s=%s\n", cr.pid, cr.uid, cr.gid, msg.name, msg.value);
if(strcmp(msg.name, ANDROID_RB_PROPERTY) == 0) {
INFO("pid %d set %s=%s\n", cr.pid, msg.name, msg.value);
reboot_pid(cr.pid);
}
#endif
//設置系統屬性
property_set((char*) msg.name, (char*) msg.value);
} else {
ERROR("sys_prop: permission denied uid:%d name:%s\n",
cr.uid, msg.name);
}
// Note: bionic's property client code assumes that the
// property server will not close the socket until *AFTER*
// the property is written to memory.
close(s);
}
freecon(source_ctx);
break;
default:
close(s);
break;
}
}
接著看property_set((char*) msg.name, (char*) msg.value)的具體實現:
int property_set(const char* name, const char* value) {
int rc = property_set_impl(name, value);
if (rc == -1) {
ERROR("property_set(\"%s\", \"%s\") failed\n", name, value);
}
return rc;
}
看來實現設置的活交給了property_set_impl(name, value):
static int property_set_impl(const char* name, const char* value) {
size_t namelen = strlen(name);
size_t valuelen = strlen(value);
//判斷屬性名的合法性
if (!is_legal_property_name(name, namelen)) return -1;
if (valuelen >= PROP_VALUE_MAX) return -1;
//如果屬性的名稱等于“selinux.reload_policy”,并且前面給它設置的值等于1,那么就表示要重新加載SEAndroid策略
if (strcmp("selinux.reload_policy", name) == 0 && strcmp("1", value) == 0) {
//加載SEAndroid策略
if (selinux_reload_policy() != 0) {
ERROR("Failed to reload policy\n");
}
} else if (strcmp("selinux.restorecon_recursive", name) == 0 && valuelen > 0) {
if (restorecon_recursive(value) != 0) {
ERROR("Failed to restorecon_recursive %s\n", value);
}
}
//查找名稱為name的屬性,如果存在的話,那么就會得到一個類型為prop_info的結構體pi,否則返回Null
prop_info* pi = (prop_info*) __system_property_find(name);
if(pi != 0) {//屬性如果存在
/* ro.* properties may NEVER be modified once set */
//如果屬性是ro.開頭,不能修改,直接返回.
if(!strncmp(name, "ro.", 3)) {
return -1;
}
//屬性可以修改,進行修改
__system_property_update(pi, value, valuelen);
} else {//屬性不存在
//屬性不存在,添加該屬性,在屬性內存區域的屬性值列表pa_info_array的最后增加一項
int rc = __system_property_add(name, namelen, value, valuelen);
if (rc < 0) {
return rc;
}
}
/* If name starts with "net." treat as a DNS property. */
//接著處理net.開頭的屬性,
//如果屬性的名稱是以“net.”開頭,但是又不等于“net.change”(net.change是一個特殊的屬性,記錄網絡屬性是否發生變化),那么就將名稱為“net.change”的屬性設置為name,表示網絡屬性發生了變化
if (strncmp("net.", name, strlen("net.")) == 0) {
if (strcmp("net.change", name) == 0) {
return 0;
}
/*
* The 'net.change' property is a special property used track when any
* 'net.*' property name is updated. It is _ONLY_ updated here. Its value
* contains the last updated 'net.*' property.
*/
//設置`net.change`屬性
property_set("net.change", name);
} else if (persistent_properties_loaded &&
strncmp("persist.", name, strlen("persist.")) == 0) {//對`persist.`屬性進行操作,該屬性應該是持久化儲存到文件
/*
* Don't write properties to disk until after we have read all default properties
* to prevent them from being overwritten by default values.
*/
//調用函數write_persistent_property執行持久化操作,以便系統下次啟動后,可以將該屬性的初始值設置為系統上次關閉時的值
write_persistent_property(name, value);
}
//發送一個屬性改變的通知,以便init進程可以執行在啟動腳本init.rc中配置的操作
property_changed(name, value);
return 0;
}
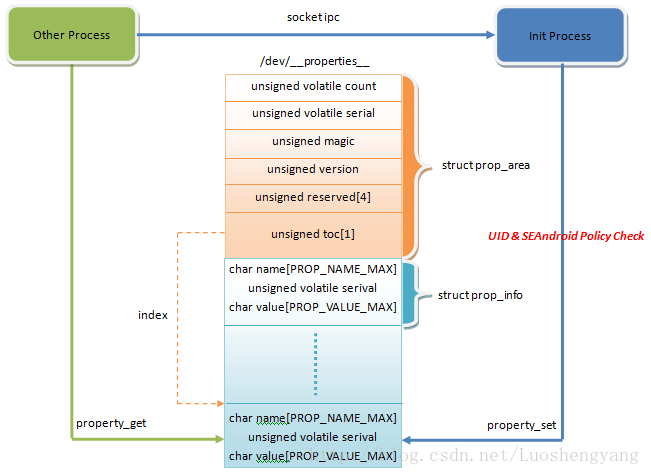
property_set_impl對以ro、net和persist開頭的屬性進行不同的處理,給張來自羅升陽blog的一張圖,幫助對android屬性服務有個整體上的認識(Android屬性的實現框架):
1.3 讀取init.rc文件
init.rc簡單介紹
init.rc是一個配置文件,內部由Android初始化語言編寫(Android Init Language)編寫的腳本,它主要包含五種類型語句:
Action、Commands、Services、Options和Import.在init.rc文件中一條語句通常占用一行,單詞之間是用空格符來相隔的。
如果一行寫不下,可以在行尾加上反斜杠,來連接下一行。也就是說,可以用反斜杠將多行代碼連接成一行代碼。并且使用#
來進行注釋。在init.rc中分成三個部分(Section),而每一部分的開頭需要指定on(Actions)、service(Services)或
import。也就是說,每一個Actions, import或 Services確定一個Section。而所有的Commands和Options只能屬于最近定義的
Section。如果Commands和 Options在第一個Section之前被定義,它們將被忽略。Actions和Services的名稱必須唯一。如果
有兩個或多個Actions或Services擁有同樣的名稱,那么init在執行它們時將拋出錯誤,并忽略這些Action和Service。
完整的init文件比較長,這里重點分析Zygote的啟動,后續要分析該進程.
下面簡單的用init.rc中的例子對Action、Commands、Services、Options和Import進行說明。
# Copyright (C) 2012 The Android Open Source Project
#
# IMPORTANT: Do not create world writable files or directories.
# This is a common source of Android security bugs.
#
#導入相關的初始化配置文件
import /init.environ.rc
import /init.usb.rc
#平臺相關的如:高通、MTK
import /init.${ro.hardware}.rc
import /init.usb.configfs.rc
#導入初始化zygote進程的配置文件
import /init.${ro.zygote}.rc
#on 對應action,是啟動,early-init市條件 write、mkdir、start是命令(commands)
on early-init
# Set init and its forked children's oom_adj.
write /proc/1/oom_score_adj -1000
# Disable sysrq from keyboard
write /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq 0
# Set the security context of /adb_keys if present.
restorecon /adb_keys
# Shouldn't be necessary, but sdcard won't start without it. http://b/22568628.
mkdir /mnt 0775 root system
# Set the security context of /postinstall if present.
restorecon /postinstall
start ueventd
#每一個service對應一個新的進程,ueventd進程名,/sbin/ueventd進程的位置(程序執行的路徑)也就是options,后面還可以跟參數,
#class、critical、seclabel都是命令
service ueventd /sbin/ueventd
//core 是服務的組,同樣名字的會在一起被啟動
class core
critical
seclabel u:r:ueventd:s0
對于這些commands在Android源碼中有文檔說明,在aosp/system/core/init/readme.txt,每個命令都有對于的代碼實現,接下來就會分析到.
有了對init.rc文件的簡單認識,回到init.cpp中,解析init.rc代碼的位置,解析init.rc主要任務由aosp/system/core/init/init_parser.cpp實現.
開始分析:
Parser& parser = Parser::GetInstance();
parser.AddSectionParser("service",std::make_unique<ServiceParser>());
parser.AddSectionParser("on", std::make_unique<ActionParser>());
parser.AddSectionParser("import", std::make_unique<ImportParser>());
Parser::GetInstance()的實現在aosp/system/core/init/init_parser.cpp:
Parser& Parser::GetInstance() {
static Parser instance;
return instance;
}
parser.AddSectionParser同樣在aosp/system/core/init/init_parser.cpp:
void Parser::AddSectionParser(const std::string& name,
std::unique_ptr<SectionParser> parser) {
section_parsers_[name] = std::move(parser);
}
這就是將service,on,import設置為了3個Section.
parser.ParseConfig("/init.rc");
這就是解析init.rc函數的入口,在init_parser.cpp里面:
bool Parser::ParseConfig(const std::string& path) {
if (is_dir(path.c_str())) {//路徑是文件夾,調用解析文件夾的函數處理
return ParseConfigDir(path);
}
//解析init.rc
return ParseConfigFile(path);
}
調用了ParseConfigFile(path):
bool Parser::ParseConfigFile(const std::string& path) {
INFO("Parsing file %s...\n", path.c_str());
//用于記錄解析init.rc的耗時
Timer t;
std::string data;
if (!read_file(path.c_str(), &data)) {
return false;
}
data.push_back('\n'); // TODO: fix parse_config.
//解析rc文件內容
ParseData(path, data);
for (const auto& sp : section_parsers_) {
//EndFile在Import_parse.cpp
sp.second->EndFile(path);
}
// Turning this on and letting the INFO logging be discarded adds 0.2s to
// Nexus 9 boot time, so it's disabled by default.
if (false) DumpState();
//打印出解析文件的耗時,用來查找耗時操作
NOTICE("(Parsing %s took %.2fs.)\n", path.c_str(), t.duration());
return true;
}
在該方法中調用的主要的方法有ParseData,EndFile接下來分別對這兩部分進行分析,ParseData:
void Parser::ParseData(const std::string& filename, const std::string& data) {
//TODO: Use a parser with const input and remove this copy
//copy數據
std::vector<char> data_copy(data.begin(), data.end());
data_copy.push_back('\0');
parse_state state;
state.filename = filename.c_str();
state.line = 0;
state.ptr = &data_copy[0];
state.nexttoken = 0;
SectionParser* section_parser = nullptr;
std::vector<std::string> args;
for (;;) {//循環遍歷解析init.rc文件內容
//next_token在system/core/init/parse.cpp
switch (next_token(&state)) {
case T_EOF:
if (section_parser) {
section_parser->EndSection();
}
return;
case T_NEWLINE:
state.line++;
if (args.empty()) {
break;
}
if (section_parsers_.count(args[0])) {
if (section_parser) {
//Section解析完成
section_parser->EndSection();
}
section_parser = section_parsers_[args[0]].get();
std::string ret_err;
//解析Action,Service, Import 三個Section
if (!section_parser->ParseSection(args, &ret_err)) {
parse_error(&state, "%s\n", ret_err.c_str());
section_parser = nullptr;
}
} else if (section_parser) {
std::string ret_err;
//解析section的內容
if (!section_parser->ParseLineSection(args, state.filename,
state.line, &ret_err)) {
parse_error(&state, "%s\n", ret_err.c_str());
}
}
args.clear();
break;
case T_TEXT:
args.emplace_back(state.text);
break;
}
}
}
重點分析!section_parser->ParseSection(args, &ret_err),section_parser->ParseLineSection,ParseSection方法在action,service,
import三個不同的section調用的位置不同:
action-->aosp/system/core/init/action.cpp:
service-->aosp/system/core/init/service.cpp
import-->aosp/system/core/init/import_parser.cpp
section_parser->ParseLineSection方法在action,service中嵌套在里面分析
依次分析這對應的三個ParseSection方法:
action ParseSection解析
ParseSection:
bool ActionParser::ParseSection(const std::vector<std::string>& args,
std::string* err) {
//將on后面的trigger觸發執行條件保存在triggers中
std::vector<std::string> triggers(args.begin() + 1, args.end());
//如果一個on后面沒有trigger將會報錯,必須要有一個
if (triggers.size() < 1) {
*err = "actions must have a trigger";
return false;
}
auto action = std::make_unique<Action>(false);
if (!action->InitTriggers(triggers, err)) {
return false;
}
action_ = std::move(action);
return true;
}
ParseLineSection:
bool ActionParser::ParseLineSection(const std::vector<std::string>& args,
const std::string& filename, int line,
std::string* err) const {
return action_ ? action_->AddCommand(args, filename, line, err) : false;
}
調用了AddCommand:
bool Action::AddCommand(const std::vector<std::string>& args,
const std::string& filename, int line, std::string* err) {
if (!function_map_) {
*err = "no function map available";
return false;
}
if (args.empty()) {
*err = "command needed, but not provided";
return false;
}
auto function = function_map_->FindFunction(args[0], args.size() - 1, err);
if (!function) {
return false;
}
AddCommand(function, args, filename, line);
return true;
}
接著調用了AddCommand(function, args, filename, line):
void Action::AddCommand(BuiltinFunction f,
const std::vector<std::string>& args,
const std::string& filename, int line) {
commands_.emplace_back(f, args, filename, line);
}
service ParseSection解析
ParseSection:
bool ServiceParser::ParseSection(const std::vector<std::string>& args,
std::string* err) {
//檢查參數個數是否合法
if (args.size() < 3) {
*err = "services must have a name and a program";
return false;
}
const std::string& name = args[1];
//檢查定義的Service名字的合法性
if (!IsValidName(name)) {
*err = StringPrintf("invalid service name '%s'", name.c_str());
return false;
}
//獲取執行文件位置和參數,也就是除了service和service名其他的參數
std::vector<std::string> str_args(args.begin() + 2, args.end());
//給service賦值
service_ = std::make_unique<Service>(name, "default", str_args);
return true;
}
定義的每個service都是一個新的進程,定義service還commands,這些commands和執行他們的方法對應關系定義是:
Service::OptionHandlerMap::Map& Service::OptionHandlerMap::map() const {
constexpr std::size_t kMax = std::numeric_limits<std::size_t>::max();
static const Map option_handlers = {
{"class", {1, 1, &Service::HandleClass}},
{"console", {0, 0, &Service::HandleConsole}},
{"critical", {0, 0, &Service::HandleCritical}},
{"disabled", {0, 0, &Service::HandleDisabled}},
{"group", {1, NR_SVC_SUPP_GIDS + 1, &Service::HandleGroup}},
{"ioprio", {2, 2, &Service::HandleIoprio}},
{"keycodes", {1, kMax, &Service::HandleKeycodes}},
{"oneshot", {0, 0, &Service::HandleOneshot}},
{"onrestart", {1, kMax, &Service::HandleOnrestart}},
{"seclabel", {1, 1, &Service::HandleSeclabel}},
{"setenv", {2, 2, &Service::HandleSetenv}},
{"socket", {3, 6, &Service::HandleSocket}},
{"user", {1, 1, &Service::HandleUser}},
{"writepid", {1, kMax, &Service::HandleWritepid}},
};
return option_handlers;
}
ParseLineSection:
bool ServiceParser::ParseLineSection(const std::vector<std::string>& args,
const std::string& filename, int line,
std::string* err) const {
return service_ ? service_->HandleLine(args, err) : false; //service_為true, 調用HandleLine
}
接著調用了HandleLine:
bool Service::HandleLine(const std::vector<std::string>& args, std::string* err) {
if (args.empty()) {
*err = "option needed, but not provided";
return false;
}
static const OptionHandlerMap handler_map; //獲得option對應的函數表
auto handler = handler_map.FindFunction(args[0], args.size() - 1, err); //根據option獲取對應的函數名
if (!handler) {
return false;
}
return (this->*handler)(args, err);
}
EndSection:
void ServiceParser::EndSection() {
if (service_) {
ServiceManager::GetInstance().AddService(std::move(service_));
}
}
void ServiceManager::AddService(std::unique_ptr<Service> service) {
Service* old_service = FindServiceByName(service->name());
if (old_service) { //service已經被定義過了就拋棄
ERROR("ignored duplicate definition of service '%s'",
service->name().c_str());
return;
}
services_.emplace_back(std::move(service)); //將service添加services_列表
}
import ParseSection解析
bool ImportParser::ParseSection(const std::vector<std::string>& args,
std::string* err) {
//import 命令是2參數的,如果參數個數不對就直接報錯
if (args.size() != 2) {
*err = "single argument needed for import\n";
return false;
}
std::string conf_file;
//第一個參數都是import,args[1]才是要導入的配置文件conf_file
bool ret = expand_props(args[1], &conf_file);
if (!ret) {
*err = "error while expanding import";
return false;
}
INFO("Added '%s' to import list\n", conf_file.c_str());
//將所有的conf_file添加到imports_列表
imports_.emplace_back(std::move(conf_file));
return true;
}
終于把ParseData方法粗略的過了一遍,接下來分析EndFile,該方法其實就在import_parser.cpp中:
void ImportParser::EndFile(const std::string& filename) {
auto current_imports = std::move(imports_); //獲取imports_
imports_.clear(); //將imports_列表清空
for (const auto& s : current_imports) { //遍歷列表
if (!Parser::GetInstance().ParseConfig(s)) { //調用ParseConfig函數,對其他配置進行解析, 流程遇上面的相同
ERROR("could not import file '%s' from '%s': %s\n",
s.c_str(), filename.c_str(), strerror(errno));
}
}
}
到此,init.rc文件的解析工作完成,接下來的的工作就是執行這些配置,由于init.rc里面配置了太多,接下來以Zygote這個service為例,分析.
在init.rc里import /init.${ro.zygote}.rc,這就引入了不同的zygote配置:
init.zygote32_64.rc init.zygote32.rc init.zygote64_32.rc init.zygote64.rc
這里以init.zygote32.rc為例:
#zygote是進程
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
#啟動組名,同樣名字的一起啟動
class main
socket zygote stream 660 root system
#onrestart表示zygote重啟時需要執行的命令
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks /dev/stune/foreground/tasks
通過對這個叫zygote的service的解析之后,在init.rc配置文件中配置了怎么去啟動zygote:
on nonencrypted
# A/B update verifier that marks a successful boot.
exec - root -- /system/bin/update_verifier nonencrypted
#通過class_start方法啟動了main(這就是zygote的中配置的)
class_start main
class_start late_start
找到class_start對應執行的函數就可以接著分析了,對應關系就在aosp/system/core/init/builtins.cpp:
ltinFunctionMap::Map& BuiltinFunctionMap::map() const {
constexpr std::size_t kMax = std::numeric_limits<std::size_t>::max();
static const Map builtin_functions = {
{"bootchart_init", {0, 0, do_bootchart_init}},
{"chmod", {2, 2, do_chmod}},
{"chown", {2, 3, do_chown}},
{"class_reset", {1, 1, do_class_reset}},
{"class_start", {1, 1, do_class_start}},
{"class_stop", {1, 1, do_class_stop}},
{"copy", {2, 2, do_copy}},
{"domainname", {1, 1, do_domainname}},
{"enable", {1, 1, do_enable}},
{"exec", {1, kMax, do_exec}},
{"export", {2, 2, do_export}},
{"hostname", {1, 1, do_hostname}},
{"ifup", {1, 1, do_ifup}},
{"init_user0", {0, 0, do_init_user0}},
{"insmod", {1, kMax, do_insmod}},
{"installkey", {1, 1, do_installkey}},
{"load_persist_props", {0, 0, do_load_persist_props}},
{"load_system_props", {0, 0, do_load_system_props}},
{"loglevel", {1, 1, do_loglevel}},
{"mkdir", {1, 4, do_mkdir}},
{"mount_all", {1, kMax, do_mount_all}},
{"mount", {3, kMax, do_mount}},
{"powerctl", {1, 1, do_powerctl}},
{"restart", {1, 1, do_restart}},
{"restorecon", {1, kMax, do_restorecon}},
{"restorecon_recursive", {1, kMax, do_restorecon_recursive}},
{"rm", {1, 1, do_rm}},
{"rmdir", {1, 1, do_rmdir}},
{"setprop", {2, 2, do_setprop}},
{"setrlimit", {3, 3, do_setrlimit}},
{"start", {1, 1, do_start}},
{"stop", {1, 1, do_stop}},
{"swapon_all", {1, 1, do_swapon_all}},
{"symlink", {2, 2, do_symlink}},
{"sysclktz", {1, 1, do_sysclktz}},
{"trigger", {1, 1, do_trigger}},
{"verity_load_state", {0, 0, do_verity_load_state}},
{"verity_update_state", {0, 0, do_verity_update_state}},
{"wait", {1, 2, do_wait}},
{"write", {2, 2, do_write}},
};
return builtin_functions;
}
對于在rc配置文件中的commands都對應一個方法函數,可以通過grep -nr "<command>" .在aosp/system/core/init/中搜索.
找到需要的對應關系:
{"class_start", {1, 1, do_class_start}},
進入do_class_start方法:
static int do_class_start(const std::vector<std::string>& args) {
/* Starting a class does not start services
* which are explicitly disabled. They must
* be started individually.
*/
ServiceManager::GetInstance().
ForEachServiceInClass(args[1], [] (Service* s) { s->StartIfNotDisabled(); });
return 0;
}
接著看StartIfNotDisabled(),位置aosp/system/core/init/service.cpp:
bool Service::StartIfNotDisabled() {
if (!(flags_ & SVC_DISABLED)) {
return Start();
} else {
flags_ |= SVC_DISABLED_START;
}
return true;
}
還調了Start(),接著看吧:
bool Service::Start() {
......
//判斷需要啟動的Service的對應的執行文件是否存在,不存在則不啟動該Service
struct stat sb;
if (stat(args_[0].c_str(), &sb) == -1) {
ERROR("cannot find '%s' (%s), disabling '%s'\n",
args_[0].c_str(), strerror(errno), name_.c_str());
flags_ |= SVC_DISABLED;
return false;
}
......
//每一個service都是一個新進程,必然需要fork
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
umask(077);
for (const auto& ei : envvars_) {
add_environment(ei.name.c_str(), ei.value.c_str());
}
for (const auto& si : sockets_) {
int socket_type = ((si.type == "stream" ? SOCK_STREAM :
(si.type == "dgram" ? SOCK_DGRAM :
SOCK_SEQPACKET)));
const char* socketcon =
!si.socketcon.empty() ? si.socketcon.c_str() : scon.c_str();
int s = create_socket(si.name.c_str(), socket_type, si.perm,
si.uid, si.gid, socketcon);
if (s >= 0) {
PublishSocket(si.name, s);
}
}
......
//execve執行程序,在`init.zygote32.rc`里寫了zygote的進程程序的位置以及參數
if (execve(args_[0].c_str(), (char**) &strs[0], (char**) ENV) < 0) {
ERROR("cannot execve('%s'): %s\n", args_[0].c_str(), strerror(errno));
}
_exit(127);
}
......
NotifyStateChange("running");
return true;
}
在fork出來的新的子進程里就會進入java層面,aosp/frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp的main()函數:
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
if (prctl(PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS, 1, 0, 0, 0) < 0) {
// Older kernels don't understand PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS and return
// EINVAL. Don't die on such kernels.
if (errno != EINVAL) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS failed: %s", strerror(errno));
return 12;
}
}
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
// Process command line arguments
// ignore argv[0]
argc--;
argv++;
......
if (zygote) {//經過一系列的初始化和參數判斷,會調用到這里
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
return 10;
}
}
最終使用runtime.start執行"com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",接著分析runtime.start的具體實現.runtime是AppRuntime類,可是AppRuntime
類沒有start方法,于是找到AppRuntime的父類AndroidRuntime的start方法:
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
ALOGD(">>>>>> START %s uid %d <<<<<<\n",
className != NULL ? className : "(unknown)", getuid());
static const String8 startSystemServer("start-system-server");
/*
* 'startSystemServer == true' means runtime is obsolete and not run from
* init.rc anymore, so we print out the boot start event here.
*/
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
if (options[i] == startSystemServer) {
/* track our progress through the boot sequence */
const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000;
LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START, ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
}
}
const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
if (rootDir == NULL) {
rootDir = "/system";
if (!hasDir("/system")) {
LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /android does not exist.");
return;
}
setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);
}
//const char* kernelHack = getenv("LD_ASSUME_KERNEL");
//ALOGD("Found LD_ASSUME_KERNEL='%s'\n", kernelHack);
/* start the virtual machine */
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
JNIEnv* env;
//啟動虛擬機
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
//注冊JNI方法到虛擬機
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
}
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {//啟動com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
free(slashClassName);
ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
mVMShutdown = true;
if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
}
該方法做了一下幾件事:
- 啟動java虛擬機
- 將JNI方法注冊到java虛擬機
- 進入到ZygoteInit.java的main()方法
進入到ZygoteInit.java也就是進入到java層,在分析Zygote的啟動過程中再接著分析,這里告一段落.需要注意的是Zygote進程的啟動是在解析init.Zygote32.rc開始的,
到這里還沒有完成,只是到這,C++層的執行完了.在另一篇介紹Zygote啟動的文章中,再接著ZygoteInit.java的main()分析,從java層分析.在C++層只是講Zygote進程創建,
但是什么活也沒干,干活是在java層面,因此文章將zygote進程的分析從此處分成兩個部分,同事也是為了讓文章內容是以init進程分析為主.
總結
本文主要分析了,init進程的啟動,主要分析了一下內容:
- init進程啟動屬性服務的過程,分析了屬性服務建立過程
- init進程對rc配置文件的解析,分為對import,action,service,commands的的解析
- 以zygote進程為例子,分析了作為service被解析之后的執行過程,一直到調用到java層的過程
參考blog
http://blog.csdn.net/fu_kevin0606/article/details/53339001
http://blog.csdn.net/innost/article/details/47204675
http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/38102011
http://blog.csdn.net/itachi85/article/details/54783506
http://blog.csdn.net/kc58236582/article/details/52247547
http://blog.csdn.net/fu_kevin0606/article/details/53320515